Signal Processing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Signal processing is an
Signal processing is an
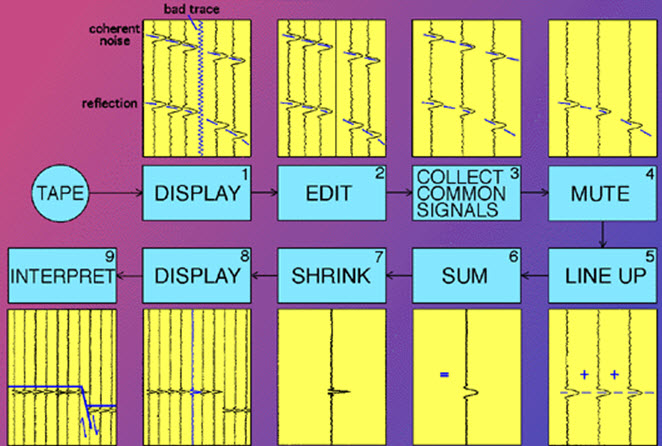 *
*
Statistical Signal Processing lecture notes at the University of Waterloo, Canada. *
Signal Processing for Communications
– free online textbook by Paolo Prandoni and Martin Vetterli (2008)
Scientists and Engineers Guide to Digital Signal Processing
– free online textbook by Stephen Smith {{Authority control Mass media technology Telecommunication theory
 Signal processing is an
Signal processing is an electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signal
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing' ...
s'', such as sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the ...
, images
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
, and scientific measurements
In mathematics and empirical science, quantification (or quantitation) is the act of counting and measuring that maps human sense observations and experiences into quantity, quantities. Quantification in this sense is fundamental to the scientific ...
. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, digital storage efficiency, correcting distorted signals, subjective video quality
Subjective video quality is video quality as experienced by humans. It is concerned with how video is perceived by a viewer (also called "observer" or "subject") and designates their opinion on a particular video sequence. It is related to the fiel ...
and to also detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal.
History
According to Alan V. Oppenheim andRonald W. Schafer
Ronald W. Schafer (born February 17, 1938) is an electrical engineer notable for his contributions to digital signal processing.
After receiving his Ph.D. degree at Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1968, he joined the Acoustics Research ...
, the principles of signal processing can be found in the classical numerical analysis
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation (as opposed to symbolic computation, symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics). It is the study of ...
techniques of the 17th century. They further state that the digital refinement of these techniques can be found in the digital control system
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial c ...
s of the 1940s and 1950s.
In 1948, Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American people, American mathematician, electrical engineering, electrical engineer, and cryptography, cryptographer known as a "father of information theory".
As a 21-year-o ...
wrote the influential paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication
"A Mathematical Theory of Communication" is an article by mathematician Claude E. Shannon published in '' Bell System Technical Journal'' in 1948. It was renamed ''The Mathematical Theory of Communication'' in the 1949 book of the same name, a sm ...
" which was published in the Bell System Technical Journal
The ''Bell Labs Technical Journal'' is the in-house scientific journal for scientists of Nokia Bell Labs, published yearly by the IEEE society. The managing editor is Charles Bahr.
The journal was originally established as the ''Bell System Techn ...
. The paper laid the groundwork for later development of information communication systems and the processing of signals for transmission.
Signal processing matured and flourished in the 1960s and 1970s, and digital signal processing became widely used with specialized digital signal processor chips in the 1980s.
Categories
Analog
Analog signal processing is for signals that have not been digitized, as in most 20th-centuryradio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmit ...
, telephone, and television systems. This involves linear electronic circuits as well as nonlinear ones. The former are, for instance, passive filter
Passivity is a property of engineering systems, most commonly encountered in analog electronics and control systems. Typically, analog designers use ''passivity'' to refer to incrementally passive components and systems, which are incapable of p ...
s, active filter
An active filter is a type of analog circuit implementing an electronic filter using active components, typically an amplifier. Amplifiers included in a filter design can be used to improve the cost, performance and predictability of a filter.
...
s, additive mixers, integrator
An integrator in measurement and control applications is an element whose output signal is the time integral of its input signal. It accumulates the input quantity over a defined time to produce a representative output.
Integration is an importan ...
s, and delay lines. Nonlinear circuits include compandor
In telecommunication and signal processing, companding (occasionally called compansion) is a method of mitigating the detrimental effects of a channel with limited dynamic range. The name is a portmanteau of the words compressing and expanding, ...
s, multipliers (frequency mixer
In electronics, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is an electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and di ...
s, voltage-controlled amplifier
A variable-gain (VGA) or voltage-controlled amplifier (VCA) is an electronic amplifier that varies its gain depending on a control voltage (often abbreviated CV).
VCAs have many applications, including audio level compression, synthesizers and ...
s), voltage-controlled filter
A voltage-controlled filter (VCF) is an electronic filter whose operating characteristics (primarily cutoff frequency) can be set by an input control voltage. Voltage controlled filters are widely used in synthesizers.
A music synthesizer VCF ...
s, voltage-controlled oscillator
A microwave (12–18GHz) voltage-controlled oscillator
A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is an electronic oscillator whose oscillation frequency is controlled by a voltage input. The applied input voltage determines the instantaneous oscilla ...
s, and phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a ...
s.
Continuous time
Continuous-time signal processing is for signals that vary with the change of continuous domain (without considering some individual interrupted points). The methods of signal processing includetime domain
Time domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental data, with respect to time. In the time domain, the signal or function's value is known for all real numbers, for the cas ...
, frequency domain
In physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time. Put simply, a time-domain graph shows how a signa ...
, and complex frequency domain. This technology mainly discusses the modeling of linear time-invariant continuous system, integral of the system's zero-state response, setting up system function and the continuous time filtering of deterministic signals
Discrete time
Discrete-time signal processing is for sampled signals, defined only at discrete points in time, and as such are quantized in time, but not in magnitude. ''Analog discrete-time signal processing'' is a technology based on electronic devices such assample and hold
In electronics, a sample and hold (also known as sample and follow) circuit is an analog device that samples (captures, takes) the voltage of a continuously varying analog signal and holds (locks, freezes) its value at a constant level for a ...
circuits, analog time-division multiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input to a single output line. The sel ...
s, analog delay line
An analog delay line is a network of electrical components connected in cascade, where each individual element creates a time difference between its input and output. It operates on analog signals whose amplitude varies continuously. In the ca ...
s and analog feedback shift registers. This technology was a predecessor of digital signal processing (see below), and is still used in advanced processing of gigahertz signals.
The concept of discrete-time signal processing also refers to a theoretical discipline that establishes a mathematical basis for digital signal processing, without taking quantization error
Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping input values from a large set (often a continuous set) to output values in a (countable) smaller set, often with a finite number of elements. Rounding and ...
into consideration.
Digital
Digital signal processing is the processing of digitized discrete-time sampled signals. Processing is done by general-purposecomputer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as C ...
s or by digital circuits such as ASICs, field-programmable gate array
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware d ...
s or specialized digital signal processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on MOS integrated circuit chips. They are widely used in audio si ...
s (DSP chips). Typical arithmetical operations include fixed-point and floating-point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can b ...
, real-valued and complex-valued, multiplication and addition. Other typical operations supported by the hardware are circular buffer
In computer science, a circular buffer, circular queue, cyclic buffer or ring buffer is a data structure that uses a single, fixed-size buffer as if it were connected end-to-end. This structure lends itself easily to buffering data streams. Ther ...
s and lookup table
In computer science, a lookup table (LUT) is an array that replaces runtime computation with a simpler array indexing operation. The process is termed as "direct addressing" and LUTs differ from hash tables in a way that, to retrieve a value v wi ...
s. Examples of algorithms are the fast Fourier transform (FFT), finite impulse response
In signal processing, a finite impulse response (FIR) filter is a filter whose impulse response (or response to any finite length input) is of ''finite'' duration, because it settles to zero in finite time. This is in contrast to infinite impulse ...
(FIR) filter, Infinite impulse response
Infinite impulse response (IIR) is a property applying to many linear time-invariant systems that are distinguished by having an impulse response h(t) which does not become exactly zero past a certain point, but continues indefinitely. This is in ...
(IIR) filter, and adaptive filter
An adaptive filter is a system with a linear filter that has a transfer function controlled by variable parameters and a means to adjust those parameters according to an optimization algorithm. Because of the complexity of the optimization algorit ...
s such as the Wiener and Kalman filter
For statistics and control theory, Kalman filtering, also known as linear quadratic estimation (LQE), is an algorithm that uses a series of measurements observed over time, including statistical noise and other inaccuracies, and produces estimat ...
s.
Nonlinear
Nonlinear signal processing involves the analysis and processing of signals produced from nonlinear systems and can be in the time, frequency, or spatio-temporal domains. Nonlinear systems can produce highly complex behaviors including bifurcations,chaos
Chaos or CHAOS may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Fictional elements
* Chaos (''Kinnikuman'')
* Chaos (''Sailor Moon'')
* Chaos (''Sesame Park'')
* Chaos (''Warhammer'')
* Chaos, in ''Fabula Nova Crystallis Final Fantasy''
* Cha ...
, harmonics
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the '' fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', ...
, and subharmonics which cannot be produced or analyzed using linear methods.
Polynomial signal processing is a type of non-linear signal processing, where polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression consisting of indeterminates (also called variables) and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and positive-integer powers of variables. An exa ...
systems may be interpreted as conceptually straight forward extensions of linear systems to the non-linear case.
Statistical
Statistical signal processing is an approach which treats signals asstochastic process
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables. Stochastic processes are widely used as mathematical models of systems and phenomena that appea ...
es, utilizing their statistical
Statistics (from German: ''Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industria ...
properties to perform signal processing tasks. Statistical techniques are widely used in signal processing applications. For example, one can model the probability distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon i ...
of noise incurred when photographing an image, and construct techniques based on this model to reduce the noise in the resulting image.
Application fields
 *
* Audio signal processing
Audio signal processing is a subfield of signal processing that is concerned with the electronic manipulation of audio signals. Audio signals are electronic representations of sound waves—longitudinal waves which travel through air, consisting ...
for electrical signals representing sound, such as speech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses Phonetics, phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if ...
or music
* Image processing
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
in digital cameras, computers and various imaging systems
* Video processing In electronics engineering, video processing is a particular case of signal processing, in particular image processing, which often employs video filters and where the input and output signals are video files or video streams. Video processing tec ...
for interpreting moving pictures
* Wireless communication
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most ...
waveform generations, demodulation, filtering, equalization
* Control systems
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial c ...
* Array processing
Array processing is a wide area of research in the field of signal processing that extends from the simplest form of 1 dimensional line arrays to 2 and 3 dimensional array geometries. Array structure can be defined as a set of sensors that are sp ...
for processing signals from arrays of sensors
* Process control
An industrial process control in continuous production processes is a discipline that uses industrial control systems to achieve a production level of consistency, economy and safety which could not be achieved purely by human manual control. I ...
a variety of signals are used, including the industry standard 4-20 mA current loop
In electrical signalling an analog current loop is used where a device must be monitored or controlled remotely over a pair of conductors. Only one current level can be present at any time.
A major application of current loops is the industry d ...
* Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other ...
* Financial signal processing
Financial signal processing is a branch of signal processing technologies which applies to signals within financial markets. They are often used by quantitative analysts to make best estimation of the movement of financial markets, such as stock ...
analyzing financial data using signal processing techniques, especially for prediction purposes.
* Feature extraction
In machine learning, pattern recognition, and image processing, feature extraction starts from an initial set of measured data and builds derived values (features) intended to be informative and non-redundant, facilitating the subsequent learning a ...
, such as image understanding
Computer vision is an interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate tasks that the hum ...
and speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers with the m ...
.
* Quality improvement, such as noise reduction
Noise reduction is the process of removing noise from a signal. Noise reduction techniques exist for audio and images. Noise reduction algorithms may distort the signal to some degree. Noise rejection is the ability of a circuit to isolate an und ...
, image enhancement
Image editing encompasses the processes of altering images, whether they are digital photographs, traditional photo-chemical photographs, or illustrations. Traditional analog image editing is known as photo retouching, using tools such as ...
, and echo cancellation
Echo suppression and echo cancellation are methods used in telephony to improve voice quality by preventing echo from being created or removing it after it is already present. In addition to improving subjective audio quality, echo suppression ...
.
* Source coding including audio compression, image compression
Image compression is a type of data compression applied to digital images, to reduce their cost for storage or transmission. Algorithms may take advantage of visual perception and the statistical properties of image data to provide superior r ...
, and video compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression ...
.
* Genomic
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dim ...
signal processing
In communication systems, signal processing may occur at:
* OSI layer
The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that 'provides a common basis for the coordination of SOstandards development for the purpose of systems interconnection'. In the OSI reference model, the communications ...
1 in the seven layer OSI model, the physical layer
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer; The layer most closely associated with the physical connection between devices. This layer may be implemented by a PHY chip.
The ...
(modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the ''carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains informatio ...
, equalization, multiplexing
In telecommunications and computer networking, multiplexing (sometimes contracted to muxing) is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share a scarce resource - a ...
, etc.);
* OSI layer 2, the data link layer
The data link layer, or layer 2, is the second layer of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. This layer is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer. The data link layer p ...
(forward error correction
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, an error correction code, sometimes error correcting code, (ECC) is used for controlling errors in data over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The central idea is ...
);
* OSI layer 6, the presentation layer
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the presentation layer is layer 6 and serves as the data translator for the computer network, network. It is sometimes called the syntax layer.
Description
Within the service layering semanti ...
(source coding, including analog-to-digital conversion
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provi ...
and data compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression ...
).
Typical devices
*Filters
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component tha ...
for example analog (passive or active) or digital ( FIR, IIR, frequency domain or stochastic filter
Stochastic control or stochastic optimal control is a sub field of control theory that deals with the existence of uncertainty either in observations or in the noise that drives the evolution of the system. The system designer assumes, in a Bayes ...
s, etc.)
* Samplers and analog-to-digital converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide ...
s for signal acquisition and reconstruction, which involves measuring a physical signal, storing or transferring it as digital signal, and possibly later rebuilding the original signal or an approximation thereof.
* Signal compressors
* Digital signal processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on MOS integrated circuit chips. They are widely used in audio si ...
s (DSPs)
Mathematical methods applied
*Differential equations
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, an ...
* Recurrence relation
In mathematics, a recurrence relation is an equation according to which the nth term of a sequence of numbers is equal to some combination of the previous terms. Often, only k previous terms of the sequence appear in the equation, for a parameter ...
s
* Transform theory In mathematics, transform theory is the study of transforms, which relate a function in one domain to another function in a second domain. The essence of transform theory is that by a suitable choice of basis for a vector space a problem may be sim ...
* Time-frequency analysis for processing non-stationary signals
* Spectral estimation
In statistical signal processing, the goal of spectral density estimation (SDE) or simply spectral estimation is to estimate the spectral density (also known as the power spectral density) of a signal from a sequence of time samples of the signa ...
for determining the spectral content (i.e., the distribution of power over frequency) of a time series
*Statistical signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, di ...
analyzing and extracting information from signals and noise based on their stochastic properties
* Linear time-invariant system theory, and transform theory In mathematics, transform theory is the study of transforms, which relate a function in one domain to another function in a second domain. The essence of transform theory is that by a suitable choice of basis for a vector space a problem may be sim ...
*Polynomial signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, ...
analysis of systems which relate input and output using polynomials
* System identification and classification
*Calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithm ...
*Complex analysis
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates Function (mathematics), functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathemati ...
*Vector spaces
In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set whose elements, often called ''vectors'', may be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called ''scalars''. Scalars are often real numbers, but can ...
and Linear algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as:
:a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n=b,
linear maps such as:
:(x_1, \ldots, x_n) \mapsto a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n,
and their representations in vector spaces and through matrices.
...
*Functional analysis
Functional analysis is a branch of mathematical analysis, the core of which is formed by the study of vector spaces endowed with some kind of limit-related structure (e.g. Inner product space#Definition, inner product, Norm (mathematics)#Defini ...
*Probability
Probability is the branch of mathematics concerning numerical descriptions of how likely an Event (probability theory), event is to occur, or how likely it is that a proposition is true. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and ...
and stochastic processes
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables. Stochastic processes are widely used as mathematical models of systems and phenomena that appe ...
*Detection theory
Detection theory or signal detection theory is a means to measure the ability to differentiate between information-bearing patterns (called stimulus in living organisms, signal in machines) and random patterns that distract from the information (ca ...
*Estimation theory
Estimation theory is a branch of statistics that deals with estimating the values of parameters based on measured empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such a way that their valu ...
*Optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criterion, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfi ...
*Numerical methods
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation (as opposed to symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics). It is the study of numerical methods th ...
*Time series
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. Exa ...
* Data mining for statistical analysis of relations between large quantities of variables (in this context representing many physical signals), to extract previously unknown interesting patterns
See also
*Algebraic signal processing Algebraic signal processing (ASP) is an emerging area of theoretical signal processing (SP). In the algebraic theory of signal processing, a set of Filter (signal processing), filters is treated as an (abstract) Algebra (ring theory), algebra, a set ...
* Audio filter
An audio filter is a frequency dependent circuit, working in the audio frequency range, 0 Hz to 20 kHz. Audio filters can amplify (boost), pass or attenuate (cut) some frequency ranges. Many types of filters exist for different audio a ...
* Bounded variation
In mathematical analysis, a function of bounded variation, also known as ' function, is a real-valued function whose total variation is bounded (finite): the graph of a function having this property is well behaved in a precise sense. For a conti ...
* Digital image processing
Digital image processing is the use of a digital computer to process digital images through an algorithm. As a subcategory or field of digital signal processing, digital image processing has many advantages over analog image processing. It allo ...
* Dynamic range compression
Dynamic range compression (DRC) or simply compression is an audio signal processing operation that reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds, thus reducing or ''compressing'' an audio signal's dynamic range. Compression is ...
, companding
In telecommunication and signal processing, companding (occasionally called compansion) is a method of mitigating the detrimental effects of a channel with limited dynamic range. The name is a portmanteau of the words compressing and expanding, ...
, limiting
In electronics, a limiter is a circuit that allows signals below a specified input power or level to pass unaffected while attenuating (lowering) the peaks of stronger signals that exceed this threshold. Limiting is a type of dynamic range comp ...
, and noise gating
* Fourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, ...
* Information theory
Information theory is the scientific study of the quantification (science), quantification, computer data storage, storage, and telecommunication, communication of information. The field was originally established by the works of Harry Nyquist a ...
* Least-squares spectral analysis
Least-squares spectral analysis (LSSA) is a method of estimating a frequency spectrum, based on a least squares fit of sinusoids to data samples, similar to Fourier analysis. Fourier analysis, the most used spectral method in science, generally ...
* Non-local means
Non-local means is an algorithm in image processing for image denoising. Unlike "local mean" filters, which take the mean value of a group of pixels surrounding a target pixel to smooth the image, non-local means filtering takes a mean of all pixe ...
* Reverberation
Reverberation (also known as reverb), in acoustics, is a persistence of sound, after a sound is produced. Reverberation is created when a sound or signal is reflected causing numerous reflections to build up and then decay as the sound is abso ...
* Time series
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. Exa ...
References
Further reading
* * * * Kainam Thomas WonStatistical Signal Processing lecture notes at the University of Waterloo, Canada. *
Ali H. Sayed Ali H. Sayed (born Sao Paulo, Brazil, to parents of Lebanese people, Lebanese descent) is the dean of engineering at École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, EPFL (École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne), where he teaches and conducts resea ...
, Adaptive Filters, Wiley, NJ, 2008, .
* Thomas Kailath
Thomas Kailath (born June 7, 1935) is an electrical engineer, information theorist, control engineer, entrepreneur and the Hitachi America Professor of Engineering, Emeritus, at Stanford University. Professor Kailath has authored several books ...
, Ali H. Sayed Ali H. Sayed (born Sao Paulo, Brazil, to parents of Lebanese people, Lebanese descent) is the dean of engineering at École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, EPFL (École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne), where he teaches and conducts resea ...
, and Babak Hassibi
Babak Hassibi ( fa, بابک حسیبی, born in Tehran, Iran) is an Iranian-American electrical engineer, computer scientist, and applied mathematician who is the inaugural Mose and Lillian S. Bohn Professor of Electrical Engineering and Compu ...
, Linear Estimation, Prentice-Hall, NJ, 2000, .
External links
Signal Processing for Communications
– free online textbook by Paolo Prandoni and Martin Vetterli (2008)
Scientists and Engineers Guide to Digital Signal Processing
– free online textbook by Stephen Smith {{Authority control Mass media technology Telecommunication theory